What is RAID?
The RAID (A multiple array of disks that are independent) is a data storage system that connects multiple drives into an entire physical device. The main purpose behind RAID’s function is to boost data reliability performance, speed, and storage capacity by distributing data between diverse disks in various configurations, referred to as the RAID level.

Why Use RAID?
- Data Redundancy and Protection:
- Redundancy Some RAID levels, such as RAID 1, RAID 5, and RAID 6, prepare redundancy by duplicating or spreading data between several disks. This means that even if one disk fails, data could be recuperated from the other disks, which means there is no downtime or data loss.
- Protection RAID assists in protecting against hardware failures. In situations in which data integrity is vital for data integrity, like servers or data facilities, RAID is an essential instrument to protect data.
- Improved Performance:
- Speed: RAID configurations like RAID 0 and RAID 10 will significantly improve writing and reading speeds by dividing (striping) data across different disks. This permits parallel processing in which several disks simultaneously manage data, resulting in faster access and better system performance.
- Efficiency for high-speed data access. Such as for gaming, editing video, and managing large databases. RAID provides the necessary speed boosts.
3. Increased Storage Capacity:
- Scalability RAID allows different smaller disks to create one larger pool of storage, energetically increasing the available storage space. This is especially beneficial for environments with growing data demands since RAID lets you expand storage without replacing the hardware.
4. Cost-Effectiveness:
- A balanced RAID could be very expensive depending on the settings (e.g., RAID 10 requires more disks). However, it is an affordable way to achieve both redundancy and performance without the requirement for costly single drives. RAID 5 and RAID 6 help provide an excellent balance of cost, storage efficiency and data security.
Common Use Cases for RAID
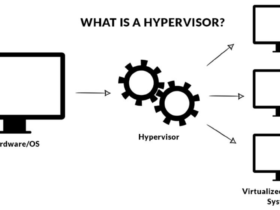
- Servers and Data main points: RAID is extensively utilized in servers to warrant mission-critical applications.You can use it as your practical purpose in Virtual Computer
- Small to Medium Enterprises (SMEs): RAID provides affordable solutions to data security and performance improvement for businesses with low IT budgets.
- High-performance computing RAID is crucial for applications that require speedy data access, such as gaming, video editing, and large-scale simulations.
- Home and Personal Use RAID is employed in personal computers and home NAS (Network Attached Storage) systems. It provides data backup and boost the performance of storage devices.
In short, RAID is a powerful instrument that improves data storage by providing redundant storage, enhancing storage performance, increasing capacity, and providing the most cost-effective solution to individuals and businesses.






Leave a Reply