Computer Processor Introduction
The computer processor, also called the central processing unit (CPU), serves as the central brain for every computer system. Knowing the role of the CPU is vital if you’re preparing for the CompTIA A+ certification. This guide will help you through the fundamental tasks of the processor. It will ensure you know the necessary information to pass the test and practical applications. Moreover, you have to detail knowledge about motherboard
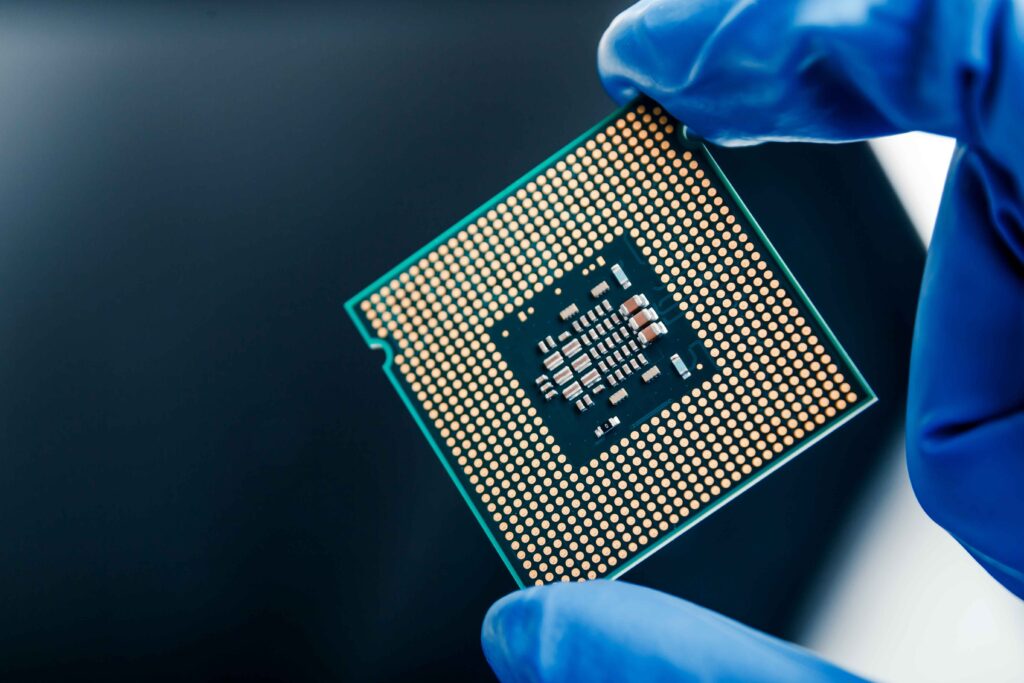
Computer processing unit definition
A processor for computers is the central part responsible for running instructions and controlling the flow of data inside the computer. It runs calculations, executes programs, and handles data, which makes it an integral component of any computer. It is attach with Motherboard.
Computer Processor’s core Functions
Instruction Fetching (IF)
- The computer processor pulls information from the computer’s memory, typically through its instruction pointer (IP) or Program Counter (PC). The processor can execute these instructions as part of the machine’s binary program.
- The Address Bus transmits information about the memory address for the processor, and the Data Bus carries instructions to the CPU. Bus for Data Bus transmits instructions.
Instruction Decoding (ID)
- After being retrieved, the instruction is passed on to an instruction decoder, which converts it into signals the CPU can comprehend. This involves breaking instructions into their operational codes ( opcode) and operand(s), which define the procedure and the data to be processed, respectively.
- Modern CPUs employ techniques such as pipelining and superscalar execution to process multiple commands at once, enhancing processing speed.
CPU data Execution (EX)
- During the execution phase, your processor’s Arithmetic-Logic Unit (ALU) or Floating Point Unit (FPU) executes the task specified in the decoded instruction. This task could involve arithmetic operations of a fundamental nature (e.g., subtraction or addition), logic functions (e.g., OR, and, OR, NOT) or more intricate tasks such as floating-point calculations.
- In modern processors, the CPU also manages branch predictions and speculation execution. It determines the direction of branches within programming and then executes the instructions ahead of time, improving the speed of processing.
Computer Processor Advanced Features
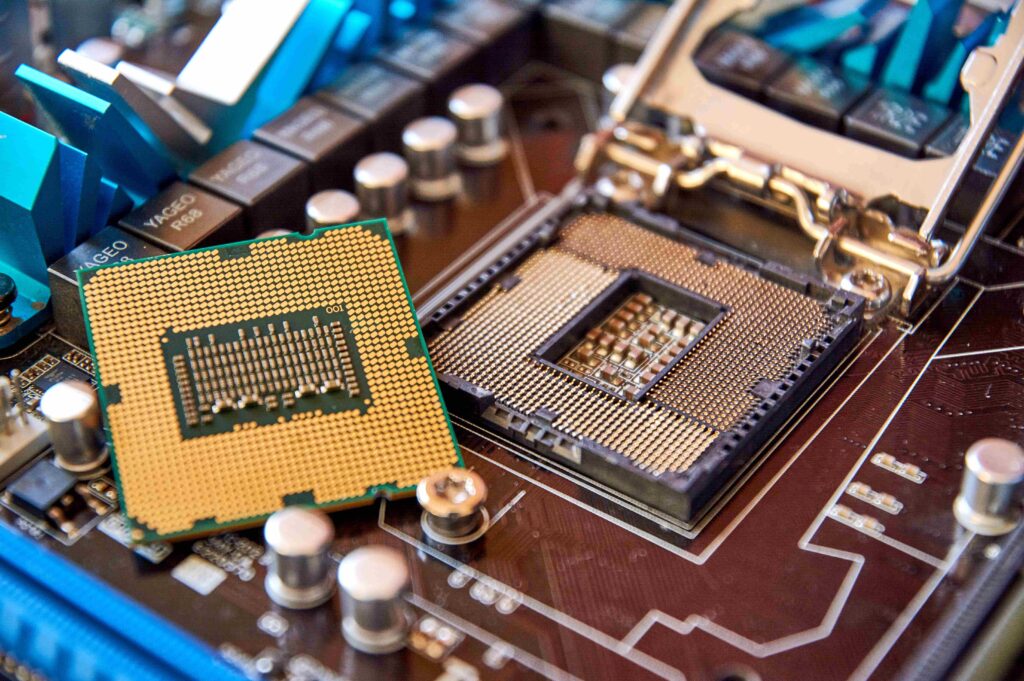
Integrated Graphics Processing Unit (GPU)
Specific CPUs have an integrated GPU that handles graphics rendering, reducing the need for a specific graphics card. This is especially beneficial in laptops and other devices in which energy efficiency and space are essential.
Thermal Management
CPUs produce heat during operation, which could affect performance and life. Thermal Design Power (TDP) is the amount of heat a processor can eliminate during a workload. Advanced cooling options like heat sinks, thermal paste or liquid cooling are frequently utilized to maintain an optimal operating temperature.
CPU Overclocking
Overclocking is the act of raising the clock speed of a CPU over its factory settings to improve performance. This requires careful monitoring of cooling and power to avoid overheating and guarantee system stability.
Hyper-Threading Technology (HTT)
Intel introduced hyper-threading, which allows a physical core to function as two logical ones, allowing the CPU to manage multiple threads at once. This allows for better multitasking and more efficient use of CPU resources.
Multicore Processing
Modern CPUs have multiple cores that can each process their instructions independently. Dual, quad, hexa, and octa-core processors, each capable of parallel processing, are all common. This greatly enhances performance, particularly in multi-threaded software.
Why Understanding CPU Functions is Crucial for the CompTIA A+ Exam
The CompTIA A+ certification tests your understanding and ability to operate with computers, including processors. Understanding how a CPU functions can help you identify hardware problems, enhance system performance, and select the appropriate components for your tasks.
Conclusion
The CPU is an essential element of every computer system. Understanding its functions is vital to anyone seeking the CompTIA A+ certification exam. Mastering the processors’ fundamentals will allow you to tackle actual IT issues and perform well in the certification test.






Leave a Reply