Motherboard is very important part of computer. You have proper wisdom about it. To buy it or taking preparetion of Comptia A+ exam. It is the CompTIA A+ certification, which is the most fundamental credential available to anyone seeking a job within IT. The most important part of the exam examines hardware components, with a particular focus on motherboards. Understanding the motherboard’s components is vital not just to pass the exam; it is also essential for practical IT work. This article will help you understand the most critical elements of a motherboard you must know to pass the CompTIA A+ exam.
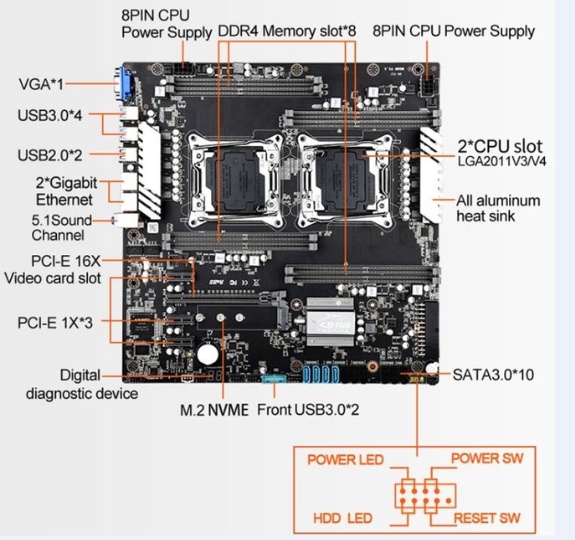
The Chipset: Controlling Communication
The chip is a crucial subject for computer motherboard. It is responsible for managing data movement between memory, processor, and other peripheral devices. It is divided into two parts:
- Northbridge is a device that handles the communication between the RAM, CPU, and high-speed devices such as graphics cards.
- Southbridge manages lower-speed peripherals such as USB ports, SATA connections, onboard music, and more.
Difference Between Northbridge and Southbridge
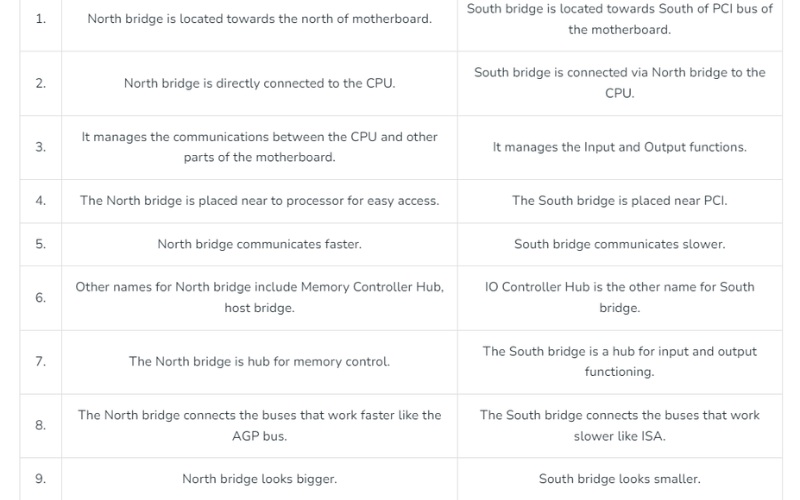
Understanding the functions of the Northbridge and Southbridge is vital to mastering motherboard-related questions on the exam.
CPU Socket: Connecting the Processor

The socket for the CPU located on the computer motherboard is responsible for determining the kind of processor that can be used. For the exam, it’s essential to know the common socket types, such as LGA 1151, for Intel processors. Additionally, AM4 is for AMD processors. AM4 for AMD processors. The type of socket affects the compatibility between the CPU and the motherboard, and it’s essential to match the right CPU to its socket.
RAM Slots: Memory Installation
RAM slots, also known as DIMM (Dual In-line Memory Module) slots, are the places where the memory of the system is located. It is the A+ exam frequently tests the knowledge of:
- Types of RAM (e.g., DDR3, DDR4)
- The amount of slots available
- How do quad-channel and dual-channel memory configurations perform
Understanding the various kinds of RAM and their different configurations is crucial to passing the exam and troubleshooting in the real world.
Expansion Slots: PCIe and Legacy Slots
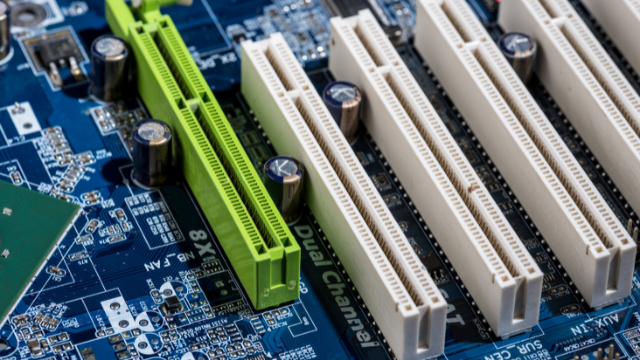
Expanding slots on a computer motherboard permits the integration of additional components like network cards, graphics cards, and storage controllers. The most commonly used kind can be found in that of the PCIe (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express) slot. To pass the exam, you must know:
- PCIe x16 slots for graphics cards
- PCIe x1 slots to accommodate smaller expansion cards
- Slots from the past, such as PCI and AGP
Understanding the purpose and difference of these slots can help you answer any questions regarding hardware upgrades and system configuration.
Storage Interfaces: SATA and M.2

The CompTIA A+ exam examines the various storage interfaces on motherboards:
- SATA (Serial ATA) ports connect traditional hard drives as well as SATA SSDs.
- M.2 slots are utilized for high-speed SSDs, which are vital for speedier data access and better system performance.
Recognizing and using these interfaces is crucial for tasks such as installing new drives or troubleshooting storage problems.
Power Connectors: Supplying Power
Computer motherboard require power connections to function:
- Its Connector for power to the ATX 24-pin is used to supply the motherboard with power.
- The power connectors for the CPU are 4-pin or 8-pin. The CPU connector supplies power directly to the processor.
In order to pass the exam, it is essential to know the purpose of these connectors and how they ensure that the CPU and motherboard get the right power.
Internal and External Connectors
Motherboards come with a variety of connectors for internal components as well as external devices:
- Connectors for internal use are headers that connect to the front USB ports, audio jacks, and system fans.
- The external connectors located on the back comprise USB ports as well as Ethernet ports and audio inputs.
Conclusion
This A+ exam will test your ability to recognize these connectors and describe their crucial purpose in tasks like building PCs or troubleshooting connectivity issues.
Knowing how motherboard components work is an essential aspect of preparation for the CompTIA A+ exam. If you know the function of the CPU socket, chipset RAM slots, and other crucial elements, you’ll be able to answer the hardware-related questions in the exam. The knowledge gained will also help you throughout your IT career, enabling you to construct upgrades, repair, and troubleshoot computers with confidence.





Excellent writing